Species profile

| Genus | Vitis |
| Species | V. tiliifolia |
| Common name | West Indian grape, Caribbean grape, water vine |
| Distribution | Mexico and many other countries in the Americas and the Caribbean (Belize, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guadeloupe, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Jamaica, Nicaragua, Panama, Puerto Rico, U.S. Virgin Islands and St Lucia) |
| Chromosome number | 2n = 38 |
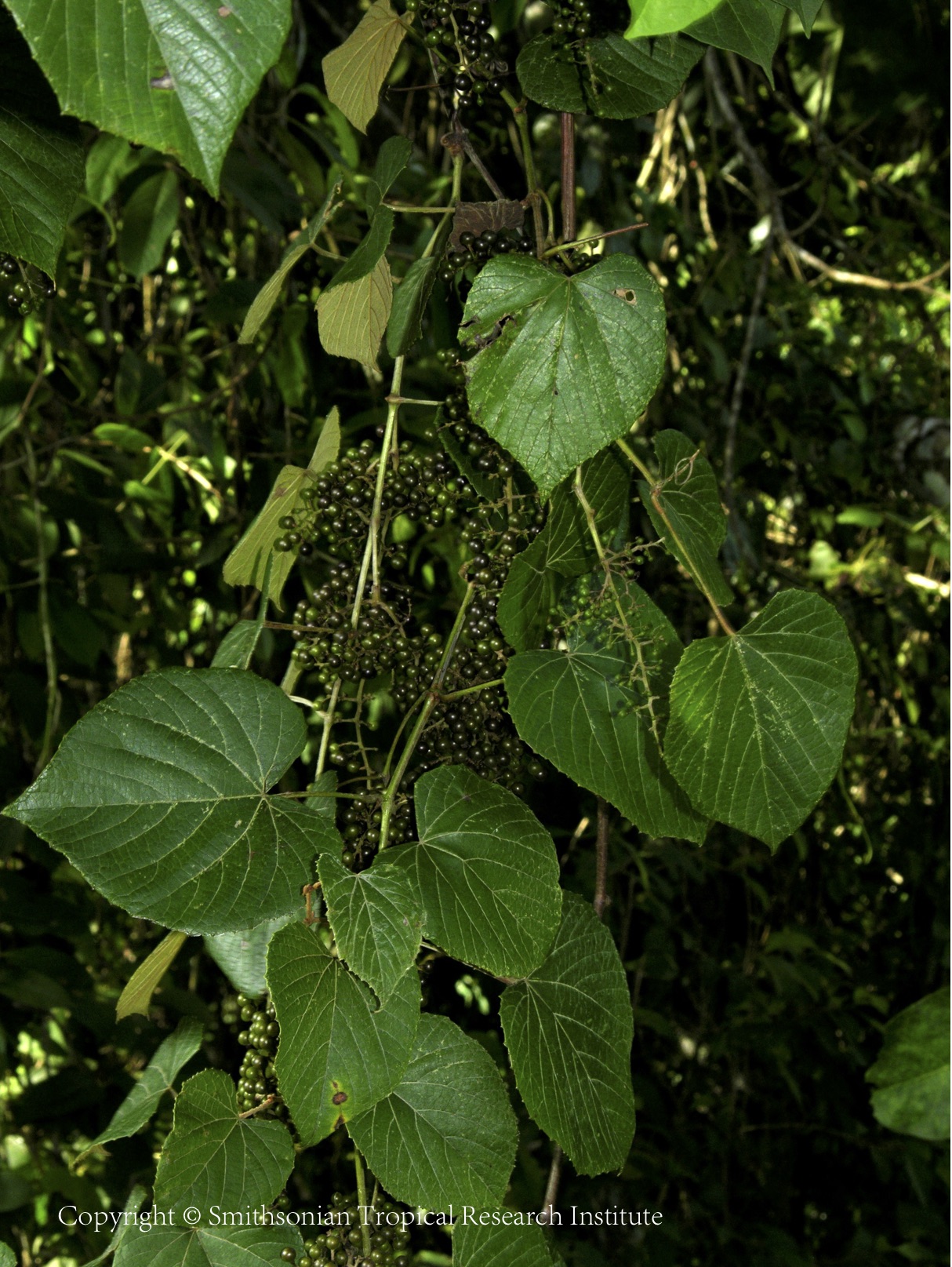
Morphological Description
It is a small to very large climbing shrub with thick, woody stems that can be 10 - 35 metres long and up to 20cm in diameter. The plant climbs into the trees and shrubs in the forest, supporting itself by means of coiled tendrils.Best known for the watery sap that can be obtained from the stems, the plant also yields a sour fruit, has local medicinal uses and can be used as cordage. The fruit, even when fully ripe, is too acid to be palatable, but it is utilized sometimes for making vinegar. The purple-black fruit is about 6 - 8mm in diameter.
Genome assembly
Germplasm
Phylogenetic tree
Population structure
ADMIXTURE
Phenotype
Reference
| Author | Title | Journal | Year | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liang Z, et al. | Whole-genome resequencing of 472 Vitis accessions for grapevine diversity and demographic history analyses | Nature Communications | 2019 | 30867414 |